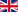
Welding refers to the joining or coating of materials using heat and/or pressure, with or without filler metal. The base materials are preferably joined in the plastic or liquid state of the welding zone - the joint is described as inseparable.
Procedures:
Gas welding with an acetylene-oxygen flame
Proceeding
Gas welding burns a mixture of fuel gas and oxygen, reaching temperatures of up to 3200°C (acetylene-oxygen mixture). Depending on the application and base material, welding is carried out with a neutral flame, oxygen or excess acetylene, whereby the filler material is added manually.
Welding gases
- Fuel gases (acetylene, propane, natural gas)
- Oxygen
Storage
Safe storage of acetylene under higher pressures is only possible if the bottle is filled with a porous mass and the porous mass contains a solvent, e.g. acetone. The porous mass absorbs the solvent like a sponge and prevents acetylene decomposition at an overpressure >1.5bar. Oxygen is stored in gaseous form in pressurized gas cylinders. Bottles with a volume of 10 to 50 litres are used.
Application
Gas welding is preferably used for welding in pipeline construction, for thin sheet metal constructions, for repair welding of cast iron and occasionally also for welding non-ferrous metals.
WMain reasons for the dissemination of the procedure
- Great mobility and handy use on construction sites
- Independence from the electrical grid
- Easy observation and control of the welding process
- There is no very complex seam preparation
- Low space requirement for the welding process
- No expensive and failure-prone equipment technology
- Good control of the position
- Good properties for bridging gaps
Metal active gas welding with cored wire electrode (136)
Procedure
An electric arc is ignited between a non-melting tungsten electrode and the workpiece, whereby the electrode and molten bath are surrounded by protective gas. The filler material is generally supplied by hand, similar to gas welding..
Equipment:
- Constant current welding unit
- non-melting electrode (tungsten)
- Burner (gas or water cooled)
- Inert protective gas (argon or helium)
- eventually a high-frequency device (for contactless ignition)
- applicable for almost all sorts of metal
- clean seams
- weld spatters are almost impossible
- hardly any rework
- Welding of very thin metal sheets is possible
- Not applicable outdoorsr
- Low welding speed
Apparatus and tank construction, pipeline construction
Arc welding
Procedure
The base material and the filler material are melted by the effect of heat from an electric arc. The arc is created when the electric current passes through the air from a meltable rod electrode to the workpiece.
Coated rod electrodes
The core wire is covered with a sheath, which has the following tasks:
- to stabilize the arc
- to protect the passing droplet and the molten bath from air ingress
- to influence the viscosity of the molten bath as well as the burning and addition of alloying elements
- to reduce the heat supply by forming a slag cover
- acidic coating A
- alkaline/basic coating B
- cellulosic coating C
- rutile coating R
- - Welding transformer (supplies alternating current)
- - Welding rectifier (supplies direct current
- - Welding transducer (supplies direct current)
Construction sites, steel construction, cast iron welding, build-up welding
Examinations:
Examination of welders according to the standard ÖNORM EN ISO 9606-1 and ÖNORM EN ISO 9606-2
Welding processes
Testing of welders for fusion welding of steels according to ÖNORM EN ISO 9606-1
- 111 Manual arc welding
- 114 Metal arc welding with flux cored electrode
- 12 Submerged arc welding
- 135 Metal active gas welding (MAG)
- 136 Metal active gas welding with cored wire electrode
- 141 Tungsten inert gas welding (TIG)
- 15 Plasma welding
- 311 Gas welding with oxygen-acetylene flame
- 131 Metal inert gas welding (MIG)
- 141 Tungsten inert gas welding (TIG)
- 15 Plasma welding
Shape and dimensions of the test pieces
Before welding, the test pieces shall be marked with the marks of the inspector and the welder. The shape and dimensions of the required test pieces shall be determined by the required scope of application. In principle, a distinction is made between four types of joints:
- Butt weld on sheet metal
- Fillet weld on sheet metal
- Butt weld on pipe
- Fillet weld on pipe
Each completed weld is visually inspected before further treatment. After successful visual inspection, additional test procedures such as radiographic, bending, breaking or dye penetration tests are carried out.
Theoretical examination
A qualification examination in the fields of welding equipment, welding processes, materials, safety and accident prevention is mandatory for welders taking the examination in Austria.
Validity
The welder's examination remains valid for 3 years (EN ISO 9606-1) or 2 years (EN ISO 9606-2), provided that the welder is regularly engaged in welding work in the applicable examination area. An interruption of 6 months is permissible.Plastic welding personnel according to ÖNORM EN 13067
Scope
This standard specifies procedures for testing the knowledge and skills of a welder who is required to carry out welding work on thermoplastics during new manufacture and repair work.
Examination
Practical examination
The welder shall manufacture the test piece specified in the subgroups next to the above in accordance with the corresponding welding instructions. All welding equipment, materials and necessary documents for completing the test piece shall be available to the welder. The time required by the welder to complete the test piece shall be the one required under production conditions.
For panels, pipes and fittings:
Group 1: PVC
Group 2: PP
Group 3: PE
Group 4: PVDF
Group 5: ECTFE or PFA or FEP
For sealing sheets:
Group 6: PVC-P
Group 7: PE
Group 8: ECB
Theoretical examination
The knowledge of the welder with regard to the practical working rules for professional and safe working must be established in the theoretical examination. This examination is carried out under the supervision of the inspector for plastic welders. The welder must answer at least 20 questions which are essential for the certification test.
Validity
A welder's examination remains valid for a period of 2 years, provided that the welder is regularly engaged in welding work. An interruption of more than 6 months is not permitteg.
Plastic welding personnel according to ÖNORM EN 13067
Scope
ÖNORM M 7807 is to be used for testing the manual dexterity and specialist knowledge of welders (plumber-pipe welders) who perform manual welding on low-pressure gas pipes for house connection pipes and inner pipes up to a maximum operating pressure of 100 mbar and a wall thickness of maximum 4.5 mm. This standard refers only to welding process 311 "Gas fusion welding with oxygen-acetylene flame".
Examination
Practical examination
Test piece 1:
Steel pipe DN 32 to DN 40 with wall thickness up to 3 mm
("left- or right-hand welding")
Test piece 2:
Steel pipe DN 80 to DN 100 with wall thickness greater than 3 mm to 4.5 mm ("right-hand weld")
On both test pieces, the weld seams shall be welded in the following welding positions - in each case without rotation of the pipe:
Seam 1: Seam half with horizontal axis in PF rising position
Seam 2: Seam half for vertical axis in PC transverse position
Specialist examination:
The theoretical part of the examination shall demonstrate to the examiner or to the inspection body the knowledge of the practical working rules required for proper and accident-free work.
Period of validity
The welder test remains valid without limitation if the following conditions are fulfilled: The testing laboratory or the welding supervisor of the company shall verify the manual skill of the welder at regular intervals on its own responsibility by means of visual and leakage tests (test pressure 1 bar), or by means of breakage tests, and shall extend the validity of the test certificate to a further 12 months in each case by means of annual entries.
If the annually documented certificates of manual skill are not available or if there is reasonable doubt as to the manual skill of the welder, the test shall be repeated.